Electrolytes play an integral part in keeping us healthy. Although often underestimated as essential nutrients, electrolytes play an integral role in maintaining cell and organ health – from fluid balance regulation to muscle contractions – our bodies rely heavily on electrolytes. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore their significance for overall well-being. Buy Fildena 120 online.
Understanding Electrolytes
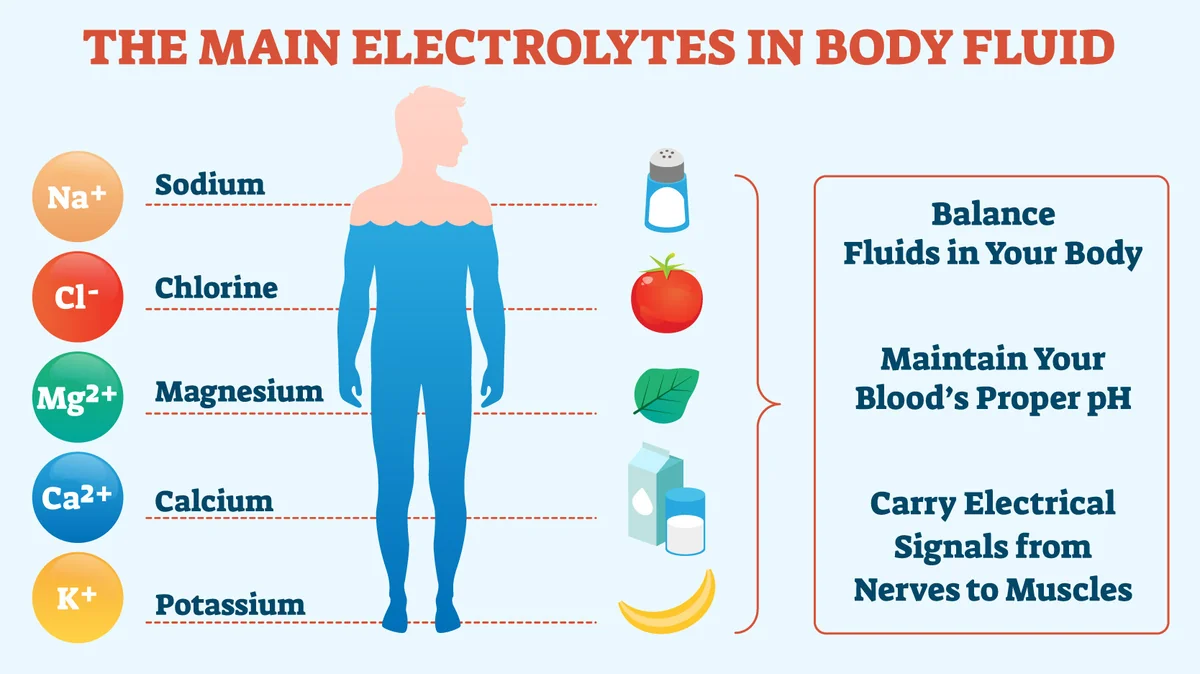
Electrolytes are minerals that carry an electric charge when dissolved in bodily fluids. Common electrolytes found within our bodies include sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium chloride, and phosphate; these work in harmony to maintain fluid balance within and outside our cells – an effect known as “osmotic balance.”
Maintaining Balanced Electrolytes
Adequate balance in terms of electrolytes is necessary for several bodily processes, including:
Muscle Function: Electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and calcium play an integral part in muscle contraction and relaxation. Without proper electrolyte balance in our systems, muscle cramping, weakness, and fatigue would ensue.
Nerve Impulse Transmission: Electrolytes enable nerve impulse transmission throughout the body, providing communication between organs and the brain. This communication plays an essential role in coordinating bodily processes like heartbeat regulation, digestion, and respiration.
Fluid Balance: Electrolytes play an essential role in maintaining fluid equilibrium within and outside our cells, which is critical to proper absorption, waste removal, and maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
Bone Health: Calcium and phosphate, two essential electrolytes, are key in building and maintaining strong bones and teeth. A deficiency can lead to osteoporosis or dental issues requiring intervention.
Acid-Base Balance: Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and chloride help the body maintain an ideal environment in our cells that enables biochemical processes to occur efficiently.
Electrolytes Come from Foods We Eat
Our bodies produce some electrolytes through various metabolic processes; however, most come from our diet. An excellent source of electrolytes would include.
Fruits and vegetables: Bananas, oranges, tomatoes, spinach, and avocados are packed with potassium, magnesium, and other electrolytes.
Dairy products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese provide calcium, sodium, and potassium; while nuts and seeds offer another good source.
Nuts: Almonds, pistachios, and pumpkin seeds contain ample magnesium as well as other vital electrolytes.
Whole grains: Wheat, brown rice, and quinoa all are great sources of both magnesium and phosphate for your daily diet needs.
Electrolyte Imbalances
Maintaining proper electrolyte balance is important, as both deficiencies and excesses of electrolytes can have negative impacts on our health.
Hyponatremia (low sodium levels): This may lead to confusion, fatigue, and possibly seizures.
Hypernatremia (high sodium levels): could potentially result in heart palpitations or seizures as severe symptoms of an imbalanced environment.
Hypokalemia (low potassium levels): This can lead to thirst, muscle cramps, and even coma in extreme cases.
Hyperkalemia (high potassium levels): This may lead to muscle cramps, weakness, and an irregular heartbeat. Numbness, tingling sensations, and potentially life-threatening heart arrhythmias may occur.
Factors Affecting Electrolyte Balance
Many factors can affect our electrolyte levels, including:
Exercise and Sweating: Intense physical activity can result in significant electrolyte losses through sweat, especially sodium and potassium.
Dietary Choices: For proper electrolyte levels to be maintained, food choices play a key role. Diets lacking fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may lead to electrolyte depletion.
Dietary choices: Additionally, certain medications (e.g. diuretics) may deplete electrolyte levels within the body. Finally, chronic illnesses may decrease electrolyte levels further.
Chronic illnesses: Kidney disease, diabetes, and Crohn’s disease can interfere with electrolyte absorption and regulation.
Maintain Balanced Electrolyte Levels
To help achieve optimal electrolyte levels, follow these strategies:
Eat a well-rounded diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources such as fish.
Drink plenty of fluids before, during, and after physical activity to replenish lost electrolytes through sweat.
Consult a healthcare professional if you suffer from any preexisting medical conditions or take medications that might alter your electrolyte levels.
Consider taking electrolyte supplements or sports drinks (in moderation) when engaging in prolonged or intense physical activities.
FAQs
1: Can drinking too much water deplete electrolytes?
A: Excessive water consumption without replenishing electrolytes can lead to hyponatremia – in which sodium levels become dangerously low – particularly concerning endurance athletes and people engaging in prolonged physical activity. This issue becomes especially troublesome during endurance events or activities requiring prolonged physical exertion.
- How often do electrolyte imbalances occur?
A: Indeed, electrolyte imbalances are rather prevalent and can result from several variables, such as dietary habits, physical activity, drug side effects, and underlying medical disorders. It is advised to regularly check electrolyte levels through blood testing, particularly for those who are more vulnerable.
3: Can electrolyte imbalances be life-threatening?
A: Electrolyte imbalances may indeed be life-threatening in severe cases. Extreme levels of sodium, potassium, or calcium may lead to seizures, coma, or irregular heartbeat requiring medical intervention if symptoms arise; medical attention should always be sought immediately if any concerning symptoms emerge.
- Are sports drinks effective ways of replenishing my electrolytes?
A: Sports drinks can be a helpful way of replenishing electrolytes lost through sweat, particularly for athletes or those engaged in prolonged physical activity. But it is wise to consume these products in moderation as many contain added sugars and calories which could deplete our reserves over time.
- Question 5: Can Dietary Supplements Help Electrolyte Imbalances?
A: Healthcare professionals may recommend specific dietary supplements containing electrolytes to solve deficiencies or imbalances; it is always advisable to speak to a qualified practitioner before beginning any supplement regimen as overdosage can also lead to problems.
Conclusion
Electrolytes play an essential part in maintaining our overall health and well-being, from maintaining fluid balance to aiding muscle contractions and nerve impulse transmission, these essential minerals play a crucial role. By eating foods high in electrolytes, staying hydrated, and treating any existing medical conditions or imbalances in our bodies, we can ensure they receive all necessary electrolytes necessary for healthy living and proper electrolyte balance is maintained – it could have far-reaching implications for overall well-being!
Home