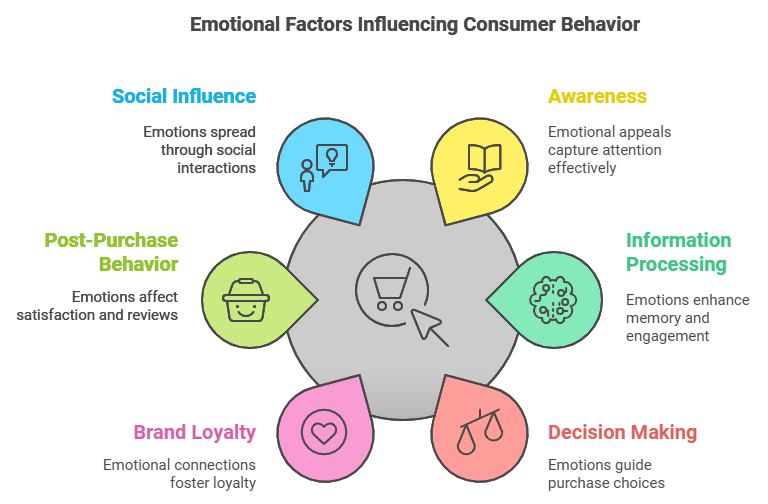
Emotion significantly influences the consumer buying process, shaping decisions at every stage. Understanding how emotions impact consumer behavior can help marketers create more effective strategies. Below are key ways emotions play a crucial role in this process.
1. Awareness and Attention
Emotional appeals in advertising can capture consumers’ attention more effectively than rational messages. Advertisements that evoke feelings—such as joy, nostalgia, or even fear—tend to stand out and create memorable impressions. For instance, a commercial that tells a heartwarming story can resonate deeply with viewers, making them more likely to remember the brand associated with that emotion.
2. Information Processing
Consumers often process information through an emotional lens. When they feel a strong emotional connection to a brand or product, they are more likely to engage with the information presented and remember it later. Emotional experiences can enhance cognitive processing, making it easier for consumers to recall brand messages and product benefits. This can lead to a more favorable evaluation of the brand.
3. Decision Making
Emotions heavily influence decision-making. Research shows that consumers often rely on their feelings rather than solely on logical reasoning when making purchases. For example, a consumer might choose a luxury car not just for its specifications but for the status and prestige it represents. Positive emotions can lead to a favorable perception of a product, while negative emotions can deter purchases. A brand that can evoke excitement or happiness is more likely to convert interest into a sale.
4. Brand Loyalty
Emotional connections foster brand loyalty. When consumers feel an emotional bond with a brand—through shared values, positive experiences, or community engagement—they are more likely to remain loyal and advocate for that brand. Brands like Apple and Nike have cultivated strong emotional ties with their customers, resulting in a dedicated fan base that often chooses their products over competitors, even at a higher price point.
5. Post-Purchase Behavior
Emotions continue to play a role even after a purchase is made. Positive emotions associated with a product can lead to satisfaction and repeat purchases. For example, a consumer who feels joy after receiving a thoughtful gift may be inclined to buy from that brand again. Conversely, negative emotions can result in buyer’s remorse, leading to returns and negative reviews. Brands that manage post-purchase emotions effectively can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
6. Social Influence
Emotions can also be contagious. Consumers are influenced by the emotions expressed by others, whether through social media, reviews, or word-of-mouth. Positive emotional experiences shared by friends or influencers can significantly impact purchasing decisions. For instance, a glowing review filled with enthusiasm can evoke similar feelings in potential buyers, prompting them to consider the product more seriously.
7. Storytelling
Brands that use storytelling effectively can evoke emotions that resonate with consumers. Narratives that connect with consumers on a personal level can enhance emotional engagement and make the brand more relatable. For example, a brand that shares stories of its impact on communities or individuals can create a deeper emotional connection, leading to increased brand loyalty and advocacy.
8. Cultural and Social Factors
Emotions are often shaped by cultural and social contexts. Marketers must understand the emotional triggers relevant to their target audience, as these can vary significantly across different demographics. For instance, humor may resonate well with younger audiences, while nostalgia might be more effective with older consumers. Tailoring emotional appeals to fit cultural norms and values can enhance their effectiveness.
9. Emotional Branding
Emotional branding is a strategy that focuses on creating an emotional connection between the consumer and the brand. This approach goes beyond traditional branding by tapping into consumers’ feelings and aspirations. Brands like Coca-Cola and Dove have successfully employed emotional branding by aligning their messages with universal human experiences, such as happiness and self-acceptance.
Conclusion
In summary, emotions are a powerful driver in the consumer buying process. Marketers who recognize and harness the emotional aspects of consumer behavior can create more compelling campaigns, foster deeper connections with their audience, and ultimately drive sales and brand loyalty. By appealing to consumers’ emotions, brands can create lasting impressions and influence purchasing decisions in meaningful ways. Understanding the intricate relationship between emotion and consumer behavior is essential for businesses aiming to thrive in a competitive marketplace.